What is a prostate?
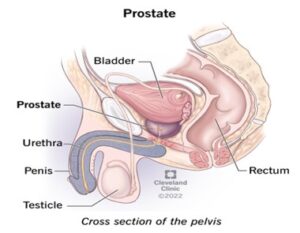
The prostate is a small gland that’s part of the male reproductive system.
Your prostate is below your bladder and in front of your rectum. Your urethra runs through the center of your prostate.
Urethra is a tube through which you pass urine.
Your prostate is about the size of a walnut, weighs about 1 ounce (30 grams)
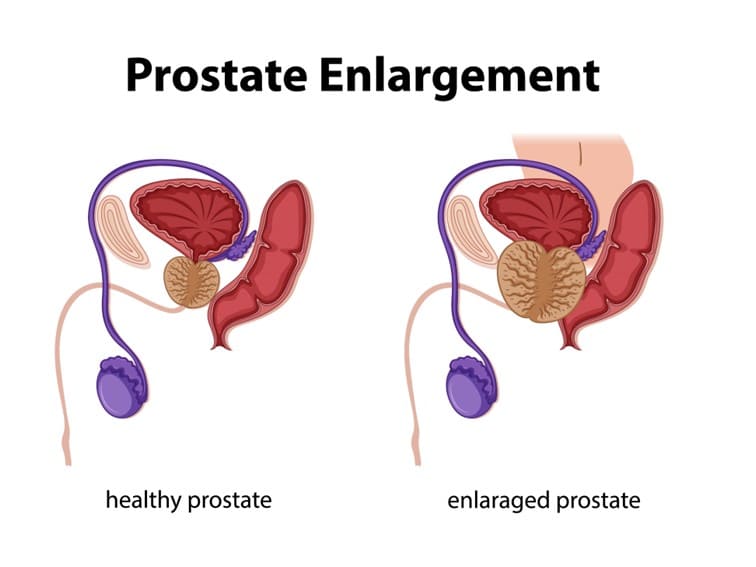
The prostate usually gets larger after age 40. It can grow from the size of a walnut to the size of a lemon.
When the prostate is enlarged it can cause some blockage to the urethra causing problems with urination.
Your prostate has five lobes: anterior (in the front) and posterior (in the back) lobes, two lateral lobes (on the sides), and one median (in the middle) lobe.
In this article, we will discuss Enlarged Prostate in detail, including its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
Enlarged Prostate
Enlarged Prostate, also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is a condition that affects a large number of men around the world.
The condition is quite common among aging men. An enlarged prostate causes a wide range of symptoms.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) isn’t cancerous, and it doesn’t increase your risk of developing prostate cancer.
Enlarged Prostate Causes
The exact enlarged prostate causes are not known, but it is believed to be related to changes in hormone levels as men age. Specifically, it is thought that an increase in the level of testosterone, a hormone produced by the prostate gland, may be responsible for the growth of the gland.
Several factors can contribute to the development of an Enlarged Prostate. Some of these factors include:
Hormonal Changes
As men age, their hormone levels change, which can cause the prostate gland to grow in size.
Age
Age is a major risk factor for Enlarged Prostate, and the condition is more common in men over the age of 50.
Genetics
If someone in your family has had an Enlarged Prostate, you may be more likely to develop the condition yourself.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle factors, such as a diet high in fat and red meat, lack of exercise, and obesity, can increase the risk of developing Enlarged Prostate.
Enlarged Prostate Symptoms
The symptoms of Enlarged Prostate can vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine flow
- Dribbling after urination
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Urgency to urinate
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Unable to pass urine
- Urinary tract infections
- Blood in the urine
Diagnosis of Enlarged Prostate
- Enlarged prostate is diagnosed by a doctor who takes a proper medical history, doing a physical examination, and various tests, including Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test and Ultrasound abdomen.
Enlarged Prostate Treatment
Treatment for Enlarged Prostate will depend on your symptoms’ severity and overall health. Some treatment options include:
Lifestyle Changes
In some cases, lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of an enlarged prostate, including:
- Reducing fluid intake before bedtime
- Avoiding caffeine and alcohol
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding medications that can worsen symptoms
Watchful Waiting
If your symptoms are mild, your doctor may recommend watchful waiting, which involves monitoring your symptoms and waiting to see if they get worse.
Medications
There are several medications that can be used to treat Enlarged Prostate.
In cases where lifestyle changes are not enough to manage the symptoms of an enlarged prostate, medications may be prescribed to improve the symptoms.
Surgery
In more severe cases, where medications are not helpful, surgery may be required to manage the symptoms of an enlarged prostate, like partial or total removal of the prostate gland
Prevention of Enlarged Prostate
While Enlarged Prostate is a common condition among aging men, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in fat and red meat
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress
- Limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption
Conclusion
Enlarged prostate is a common condition that affects men over the age of 50. As the prostate gland grows, it can put pressure on the urethra, which can cause urinary problems such as difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and incomplete emptying of the bladder.
The treatment of enlarged prostate depends on the severity of the symptoms and the impact on the patient’s quality of life.
It is recommended to consult a specialist doctor in time if you experience the signs and symptoms of enlarged prostate.
Leave a Reply