There is a growing understanding of how the environment affects the health of individuals and communities.
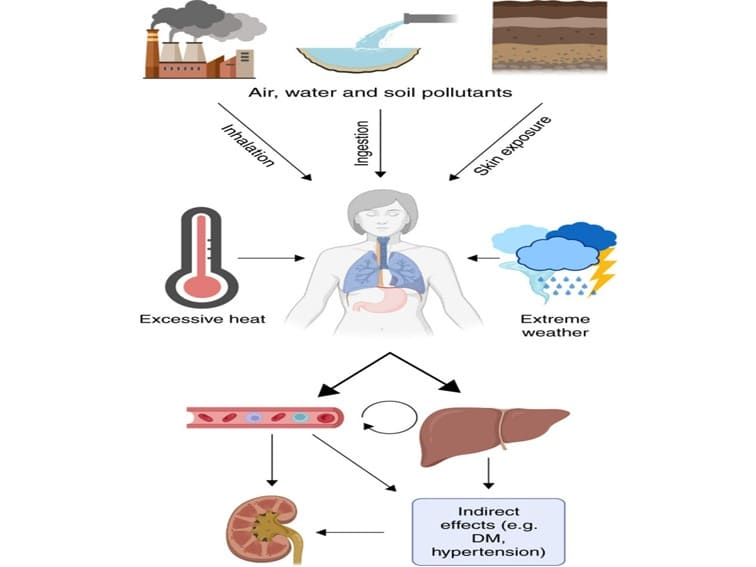
Environmental causes of kidney disease: Exposure to human-made and naturally occurring toxins in the air, water, and soil can lead to the accumulation of toxins in organs, and contribute to diseases like hypertension, diabetes and kidney disease.
People may also experience adverse health issues due to transient events such as natural disasters – floods, storms, earthquakes, and extreme cold and hot conditions.
People who have kidney disease are potentially at risk of being affected by environmental exposures.
Air
Particulate matter (PM) an air pollutant that is a complex mixture of small particles and liquid droplets arising from the combustion of fossil fuels and biomass, has come into focus for its adverse effects.
Major exposure to air pollutants occurs via gas emissions from an increasing number of vehicles on roads, industrial gases, and construction-related pollution.
Air pollutants are associated with an increased risk of specific types of kidney disease.
Short-term exposure during wildfires and burning of agricultural waste is associated with a 5% increased risk of all causes and cardiovascular mortality among patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis.
Water
Water contamination is a major source of spreading diseases. Pathogens – disease-causing germs and microbes contaminate water bodies. Nowadays, pesticides, a wide range of heavy metals, industrial chemicals and hydrocarbons, and perfluorinated compounds are common water contaminants.
Human exposure to these agents occurs through drinking water, consumption of fish or prawns living in the water, or through skin contact with the water.
Metals Exposure
Metals, including arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury, and uranium, are among the most extensively studied waterborne chemicals that are harmful to kidneys.
Arsenic is found in different regions of the world – particularly in groundwater. It is a naturally occurring metalloid. Metal smelting and mining introduce arsenic into water bodies including groundwater.
When it comes to contamination of groundwater in India – Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Manipur, and Assam are reported to be the most affected.
Long-term exposure to arsenic is causally related to increased risks of skin, lung, bladder, and kidney cancers.
According to some studies, drinking water with high levels of arsenic leads to an increased incidence of kidney disease, its progression, and an increased risk of death.
Exposure to pesticides occurs through several routes, including consumption of contaminated water, fruits, and vegetables. Farmers or agricultural workers are at increased risk of exposure
Pesticides that have been linked to kidney disease in one or more studies include the herbicides butylate, glyphosate, metolachlor, paraquat, and, and the insecticides methyl parathion and endosulfan.
Environmental causes of Kidney Disease – Extreme weather
The effect of extreme heat and natural disasters (e.g., floods, earthquakes), is expected to increase in the coming years because of climate change.
Extreme heat causes hyperthermia and dehydration leads to an increased risk of kidney injury.
The risk of kidney injury increases by doing strenuous exercise in extremely hot conditions – which may lead to muscle damage. Another risk factor for kidney damage is the intake of sugar-sweetened beverages with high fructose.
Global warming and environmental pollution are the results of human behavior. They have huge consequences on our health – particularly our kidneys’ health. We are also witnessing increasing incidences of diabetes and hypertension due to environmental pollution which eventually will lead to kidney disease.
Bottom Line
We all need to be responsible in protecting our earth and the environment and contribute towards reducing pollution to protect our health and the health of our future generations.
Leave a Reply