On the occasion of World Osteoporosis Day, let us try to understand the link between chronic kidney disease and Osteoporosis – and the measures that one should take to prevent osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disorder of the skeleton due to a reduction in bone strength. It leads to an increased predisposition for fractures. Osteoporosis affects bone quantity (characterizes the levels of bone resorption) and bone quality (internal structure of the bone). These are the two main components of bone strength. When an individual develops this condition his risk for fragility fractures increases and the individual can become prone to a wide range of health-related issues.
Chronic Kidney disease (CKD) induced osteoporosis
This condition has become a burgeoning global health issue. Osteoporosis or bone thinning is common in people with kidney disease. CKD-induced osteoporosis is a systemic disease associated with the disruption of vitamin D, hormones, and mineral homeostasis. CKD-induced osteoporosis makes an individual prone to fractures.
Risks Associated with CKD-Induced Osteoporosis
Patients with chronic kidney disease show higher osteoporosis prevalence; low vitamin D production in the body, calcium deficiency, low bone mineral density, greater fracture rates and increased risk of bone fractures (hip fractures), and increased morbidity and mortality. When the severity of chronic kidney disease increases, osteoporosis too becomes very severe. Such patients will need regular vitamin D and calcium supplements and lifestyle modifications. They are prone to higher rates of fractures.
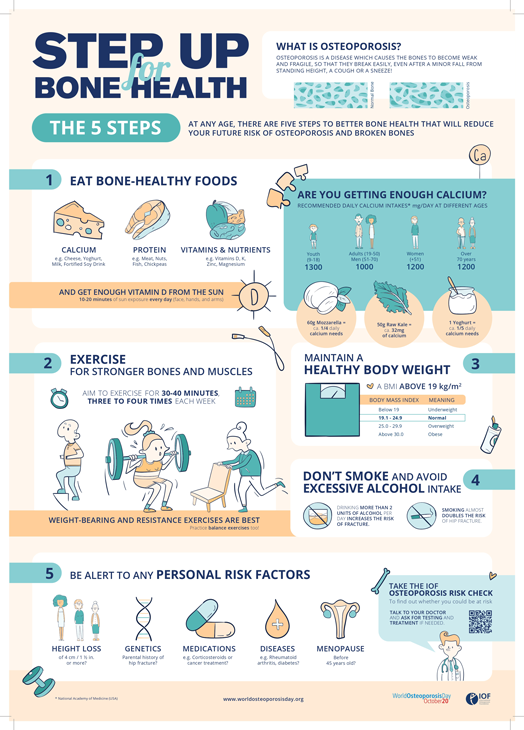
The risk of bone fractures such as hip fractures is very high (nearly double) in CKD patients older than 45 years when compared to normal healthy individuals. Owing to this factor their routine activities and quality of life get disturbed. To reduce the risk and avoid bone fractures the following steps are recommended:

Leave a Reply